Contact Stability & Safety Analysis of MRI-Actuated Intravascular Robotic Catheter
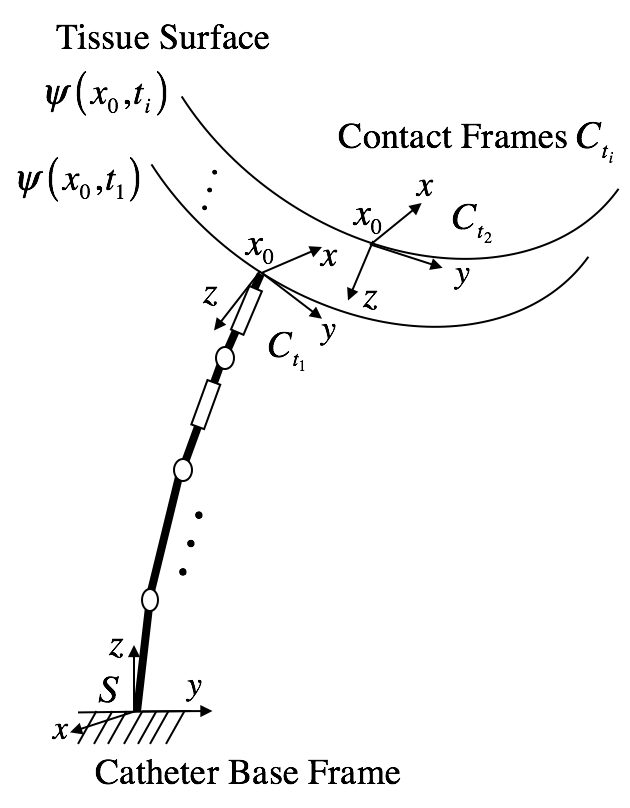
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is the cornerstone of atrial fibrillation treatment. During radiofrequency ablation, the catheter needs to maintain steady contact with the substrate tissue with appropriate contact force to create a transmural scar, in order to create a gap-free lesion. There are two major disturbances that can greatly affect the contact stability and safety during the cardiac ablation, namely, the rapid cardiac surface motion and periodic blood flow running through the heart. These two types of disturbances can potyentially lead to unpredictable lesion formation during ablation. Finding a feasible or optimal configuration of the robotic catheter to maintain a stable & safe catheter-tissue contact under the beating heart motions or the blood flow drags motivates us to investigate the contact safety and stability under these disturbances.
In this project, we investigate the contact stability & safety of the MRI-actuated intravascular robotic catheter under surface motion and blood flow disturbances. We first formulate the contact model of the PRB-modeled robotic catheter, and propose the contact stability and safety metrics under given disturbances. A stable catheter-tissue contact should maintain the contact force inside the friction cone under the disturbances, in order to reduce the possibility of sliding and positional errors. A safe catheter-tissue contact will keep the normal force within the desired force limits and will ensure the formation of a transmural lesion.
For contact stability & safety analysis under surface motion disturbances, a deterministic formulation of the contact safety and stability is presented. We further formulate a contact force actuation Jacobian that approximates the relationship between the change of the contact force and the change of the actuation of the robotic catheter, in order to perform the contact force control for achieving better contact stability and safety under the surface motion disturbances. Several contact force control algorithms and schemes are proposed and evaluated in a simulation environment using prerecorded in vivo left ventricle heart motion data.
For contact stability & safety analysis under blood flow disturbances, a probabilistic formulation of the contact safety and stability is proposed. The core idea of this research is to employ a probabilistic model to quantify the influence of the blood flow drags acted on the body of the robotic catheter, because accurately modeling the blood flow disturbance is a computationally challenging problem. Using the probablistic blood flow disturbance model, we propose the probabilistic contact stability and contact safety metrics, employing a sample based representation of the blood flow velocity distribution. We present an analysis of the contact stability and contact safety of the robotic catheter using these models in a specific example scenario under left pulmonary inferior vein (LIV) blood flow disturbances.